Ten subject areas of CFA in English

Recently, I faced CFA level 1 exam in computer based testing environment. In a previous article I have explained how to get your self ready to start venturing into CFA exams. I could share that experience even before I faced the exam, because they are ‘must go through’ stuff a new student usually face. I would highly recommend you to read this article if you are interested in the ‘getting into’ part.
My journey so far as a CFA Level I candidate in Sri Lanka
Before I started studying for CFA level 1, the subject areas included in the CFA curriculum was a mystery for me. Following are the 10 subjects tested with different weightings in the exam.
- Ethical and Professional Standards
- Quantitative Methods
- Economics
- Financial Reporting and Analysis
- Corporate Finance
- Equity Investments
- Fixed Income
- Derivatives
- Alternative Investments
- Portfolio Management
Only first six subject names gave some intuition and meaning, with the existing background when I started. I can provide some insight into each subject area with the knowledge gained from CFA level 1 studies. Subjects remain the same in CFA level 2 and 3, but I believe the subject material becomes deeper in upper levels.
Written tests measure the abilities of the candidates in level 2 and 3, while an MCQ based test is available for level 1.
Let’s dive deep into first five subjects in this article.
Ethical and Professional Standards

Ethical and professional standards section is a special section in the CFA curriculum. In the exam, candidates should make sure they do really well in this area. Keeping this as the last subject to study can be helpful, because the concepts can be easily forgotten while getting ready for the exam. It is a known fact that a large fraction of questions are based on this area.
CFA institute has formal definitions and descriptions. Candidates need to remember and by heart them.
There are Seven standards of professional conduct as well as a code of ethics that a candidate must remember. In this area, questions can be tricky even after studying the subject carefully. Important thing is to do as many questions as possible before facing the exam.
Other important part is GIPS(Global Investment Performance Standards). 50% of the time should be spent on practising questions in this area.
Quantitative Methods
Quantitative methods is a subject that tests the mathematical skills potentially required in the finance field. For me this area was the easiest to grasp because of my engineering background. Basic understanding of time value of money and high school mathematics is very important prerequisite for this subject.
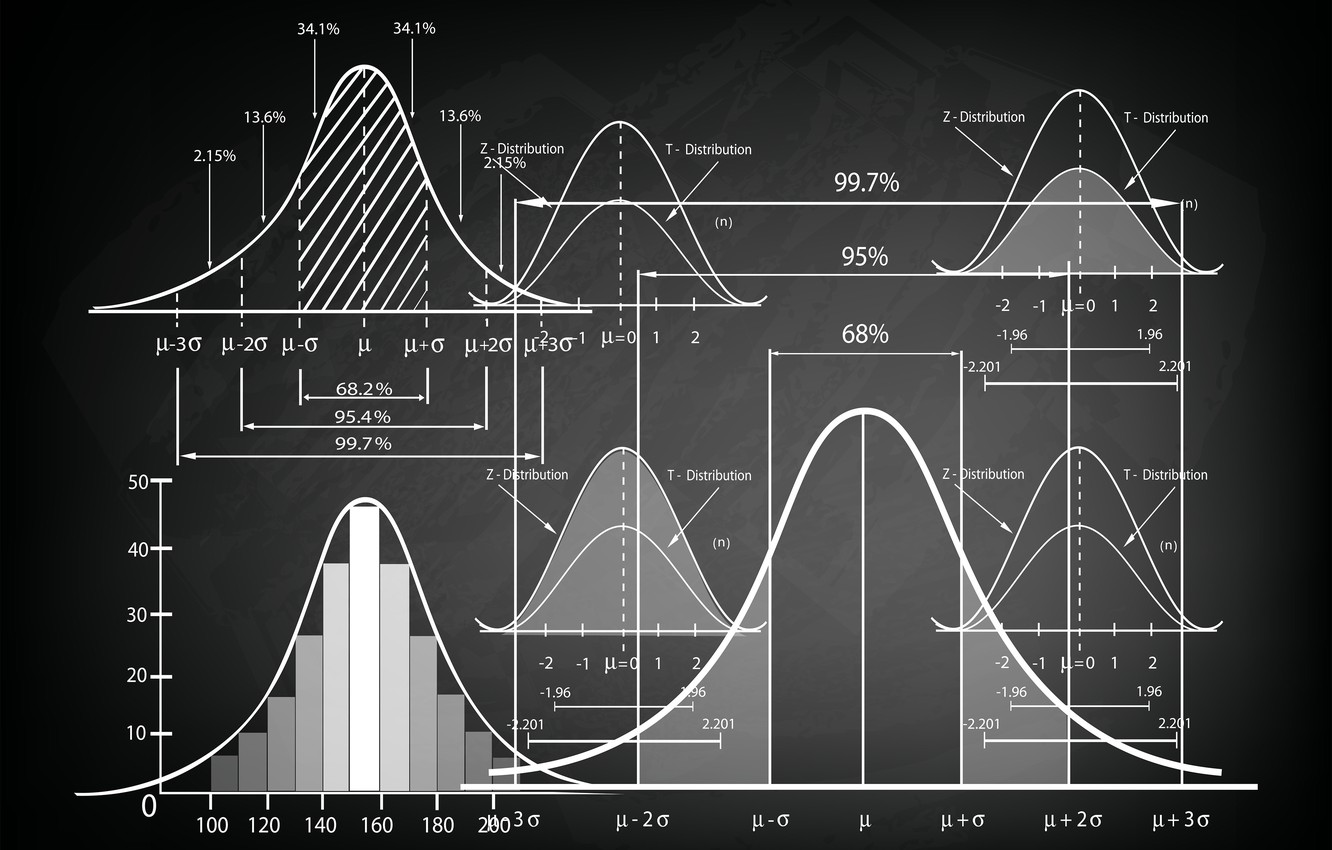
Most of the constituents, of the subject include basic statistics and probability concepts. Concepts such as mean, variance, standard deviation, central limit theorem, gaussian distribution and z scores. In probability most challenging part was understanding hypothesis testing concepts. In hypothesis testing there are many types statistical distributions to learn. Learning them can be rewarding because, these valuable concepts are not only useful in finance, but also commonly used in so many other areas.
Important thing to notice is the use of Texas Instruments BA II plus calculator. This is one of the approved calculators for this exam. A candidate must be very familiar with the calculator before facing the exam. It is very important to start learning the calculator in the quantitative methods section.
This subject takes a lot of reading time as well as some time to understand. Since the subject involves mathematical concepts, they are not easily forgotten.
Practising a lot questions should be done in the process of learning and preparing for the exam.
Economics
Economics section is a long section just like Quantitative methods section. I would say it is the most time consuming and longest subject area to study. This subject only involves basic economics concepts taught in high school and early bachelors level.

Curriculum includes concepts from both macro economics and micro economics. Starting from different market structures (perfect competition, monopolistic competition, monopoly etc), Demand and supply, Aggregate output, Business cycles, monetary and fiscal policy, international trades and currency exchange rates are the areas included in the subject.
All the sub topics are understandable, if the studying is given enough time. The problem is with the amount of sub topics, which makes it kind of hard to grab them at once. The problem is not with the depth, it is the breadth.
Most of the practice questions are confusing and some times not related to the concepts available in the curriculum. The best thing is to get familiar with many practice questions.
Financial Reporting and Analysis
Financial reporting and analysis subject is among the longest subjects in the curriculum. This subject starts from introducing different organizations that set financial reporting standards. Then the curriculum extends explaining the statement of profit and loss, balance sheet and the cash flow statement. Both GAAP(Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) and IFRS(International Financial Reporting Standards) methods are explained in each use case.

The syllabus includes reporting standards for recognizing taxation, inventories, long term liabilities and long lived assets. And also financial analysis techniques and financial reporting quality are discussed. Du Pont Analysis is an interesting concept that is mentioned in the financial analysis techniques. That single concept can increase the understanding of previously learnt concepts in a remarkable way.
Remembering all the concepts as an aggregate is the problem here. Individually all the reporting concepts are easy to understand. Remembering the standards for both GAAP and IFRS in parallel is the challenging part. Practice questions are mostly quantitative, but there are non quantitative questions testing the concepts as well.
There is a huge amount of formulae to by heart in this section. Final day before the exam is usually spent in remembering these formulae.
If you have an accounting background from a previous qualification, this will probably be an easy subject to conquer.
Corporate Finance
This is a relatively easy subject compared to first four subjects explained earlier. If you have studied an accounting related qualification or a first year bachelor in business studies, this subject will be comparatively easy. Additionally, it takes a small time to learn this subject due to few amount of chapters available.

Corporate Governance related theory, Capital budgeting, Cost of Capital, Measures of leverage and Working capital management are the main sub topics available. Since time value of money is already covered in quantitative methods, cost of capital concepts become easier to grasp.
Some amount of effort is required to by heart some concepts. In few words, this subject includes how the general functioning of a company works from a financial perspective. Most of the concepts appear as though previously covered and easy to grasp.
There are some formulae to remember in this subject. Having these formulae ready at the exam is important.
In the second part of this article, the deep dive into rest of the subjects is continued. The second article includes the subjects that become CFA specific, because subjects already explained are usually available in any business related qualification. Subjects to come in the next article are related to investment, which is the core function taught in the CFA curriculum.

